Inmarsat overview
Inmarsat operates a fleet of 14 geostationary satellites.

Short introduction
- Inmarsat plc is headquartered in London, UK. Worldwide locations.
- Founded: 1979 by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) as a UN organization
- Privatized in 1999
- Inmarsat is the abbreviation for International Maritime Satellite
Operations centers:
Inmarsat ground stations
- Auckland, New Zealand
- Burum, Netherlands
- Fucino, Italy
- Laurentides, Canada
- Lino Lakes, USA
- Nemea, Greece
- Paumalu, Hawaii (USA)
- Perth, Australia
- Warkworth, New Zealand
- Winnipeg, Canada
- Merredin, Australia
The Network Operations Center (NOC) is located in London.
Frequency band: L-band, Ka-band and S-band
Global voice and data services for land mobile, maritime and aeronautical applications
Satellite system: Inmarsat A was the first Inmarsat service introduced in 1982.
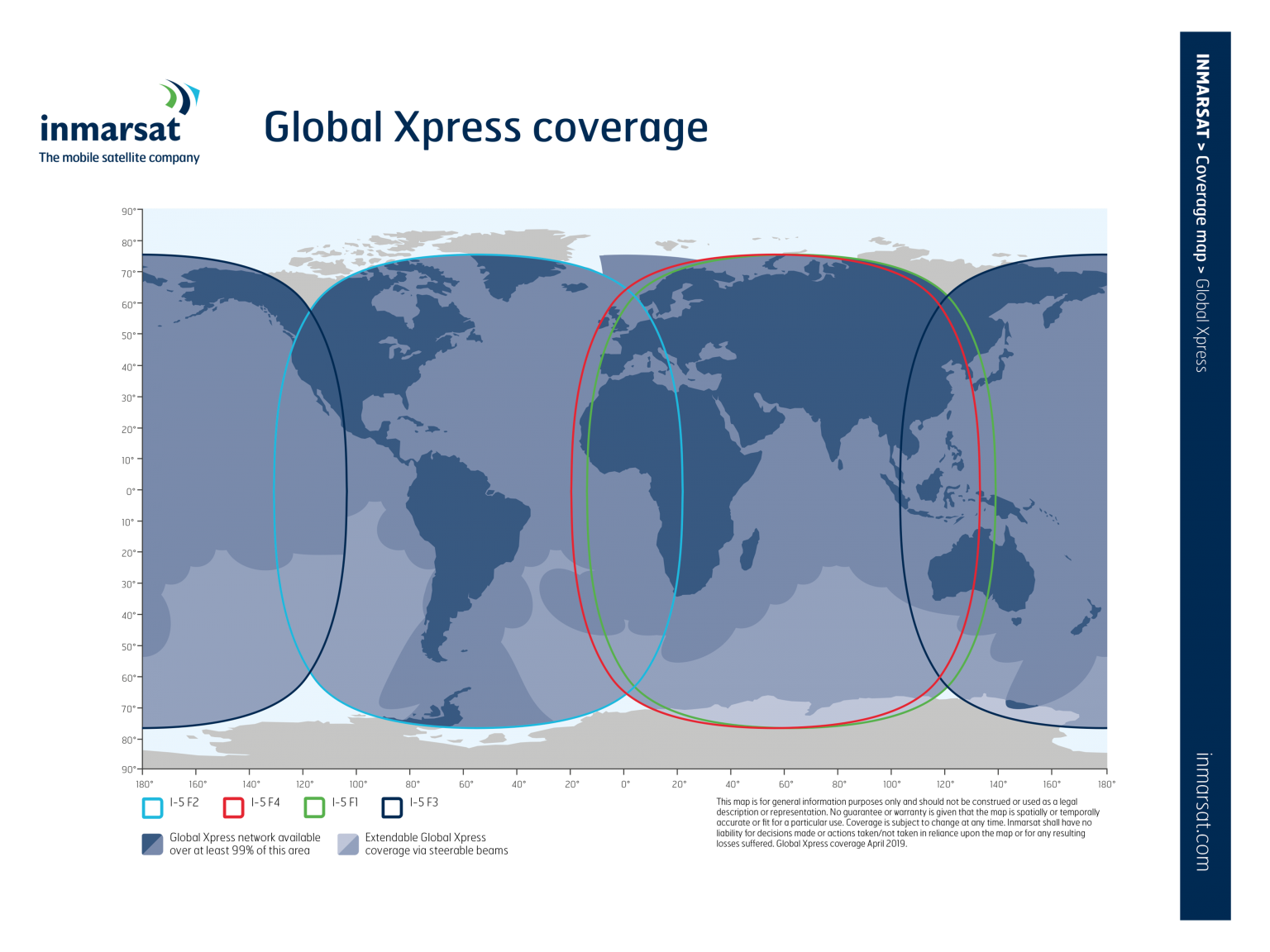
Current fleet: Inmarsat-4, Inmarsat-5 (GX1-GX4, GX5), IS EAN
Future satellites: GX6A & 6B Launch in 2020, GX7, 8 & 9 Launch in 2023, GX10 Launch in 2022.
The satellite system and its infrastructure
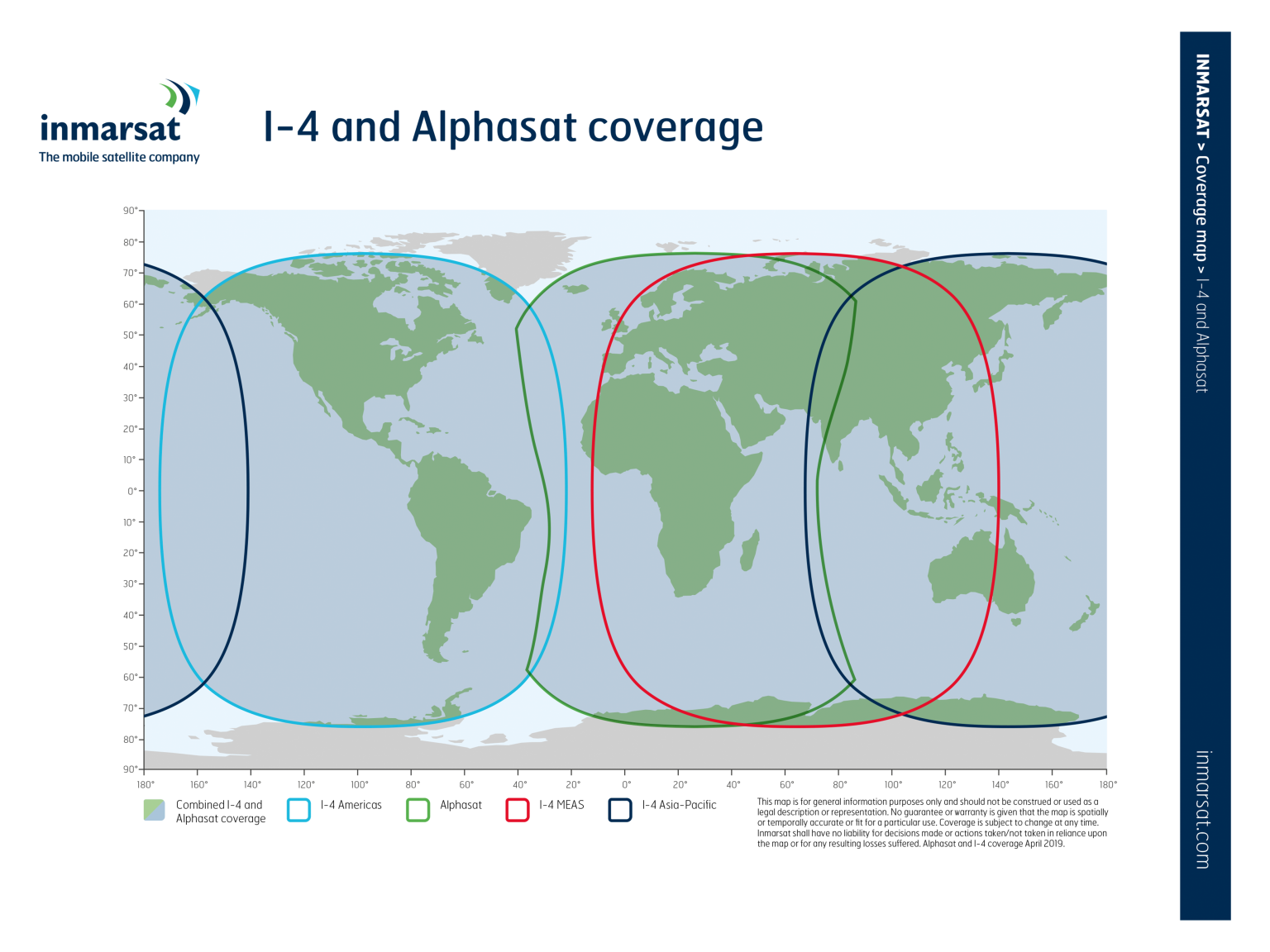
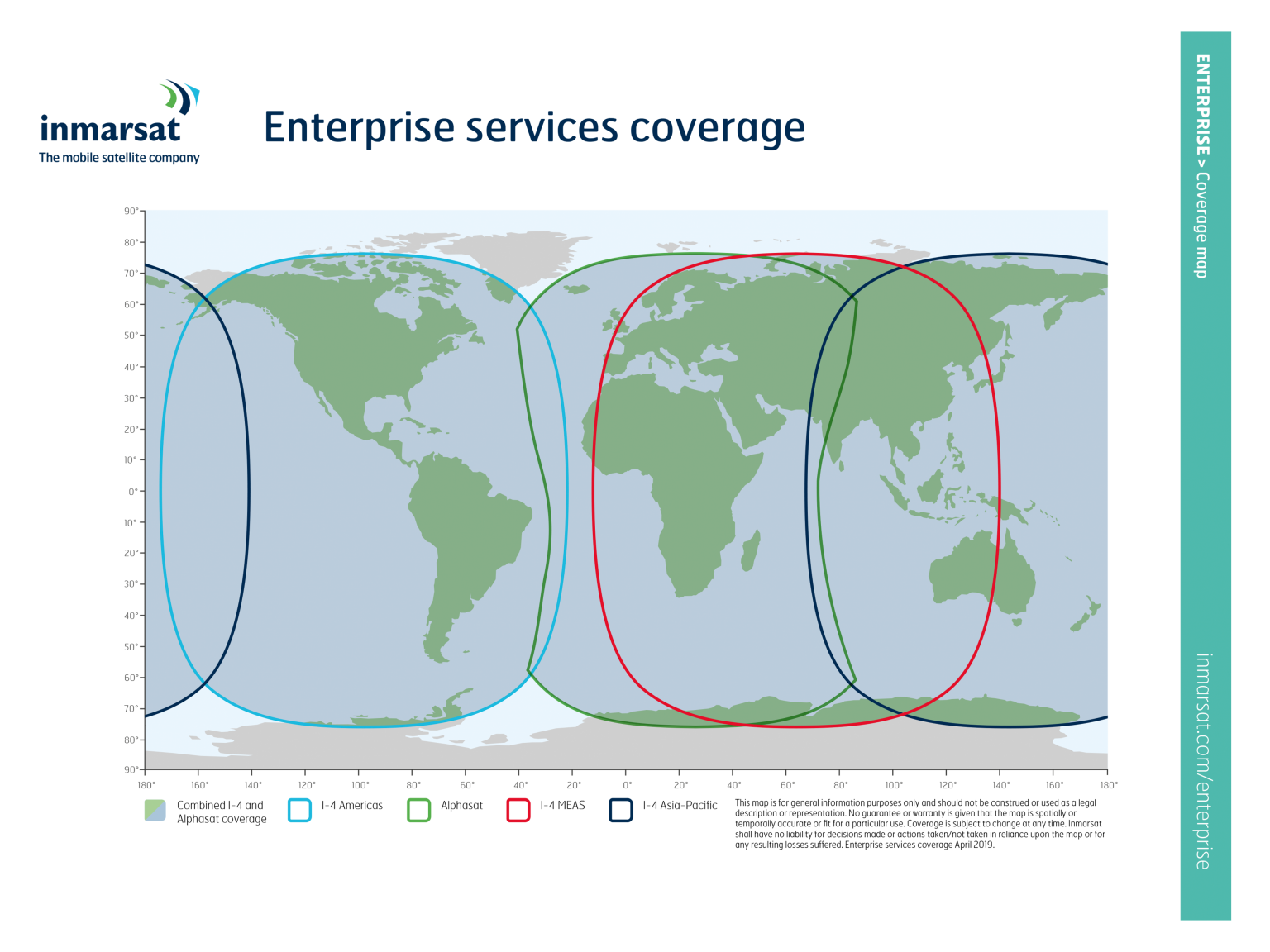
The 13 Inmarsat satellites are positioned in geostationary orbit (35,786 km above the Earth).
All voice and data connections are routed via satellite and through the ground network. Inmarsat's ground network consists of a variety of interconnected Satellite Access Stations (SAS) and data centers located at strategic locations around the world.
The SAS - also called ground stations or land ground stations (LES) - act as traffic gateways and transmit the satellite signal to terrestrial networks such as the Internet or the landline network and mobile communications. The ground network also connects signaling and other network management traffic to data centers called Meet-me Points (MMP) in New York, Amsterdam and Hong Kong.
Network Operations Center (NOC)
The Network Operations Center (NOC) at Inmarsat headquarters in London is responsible for coordinating all network activities and permanently monitoring the ground network.
Through intelligent bandwidth and frequency management, the NOC team can increase the available capacity if necessary - for example in the event of a natural disaster, when demand for voice and data connections via satellite increases in a certain region.
Land mobile services
- Global Xpress: LX (Land Xpress)
- Broadband: IsatHub, BGAN, BGAN HDR, BGAN Link
- Voice: GSPS, GSPS Link, BGAN
- M2M: BGAN M2M, IsatData Pro, Isat M2M

Overview of satellite systems
The satellite systems are Inmarsat, Iridium, Thuraya, Globalstar, Echo-Star and various VSAT providers such as Eutelsat.
The various satellite systems differ, among other things, in:
- The type/positioning of the satellites (LEOs, MEOs, GEOs)
- The frequency band
- Your coverage
- The data bandwidth
- The connection quality
- The size of the end devices
- The prices of the devices
- Operating permits
- Import restrictions